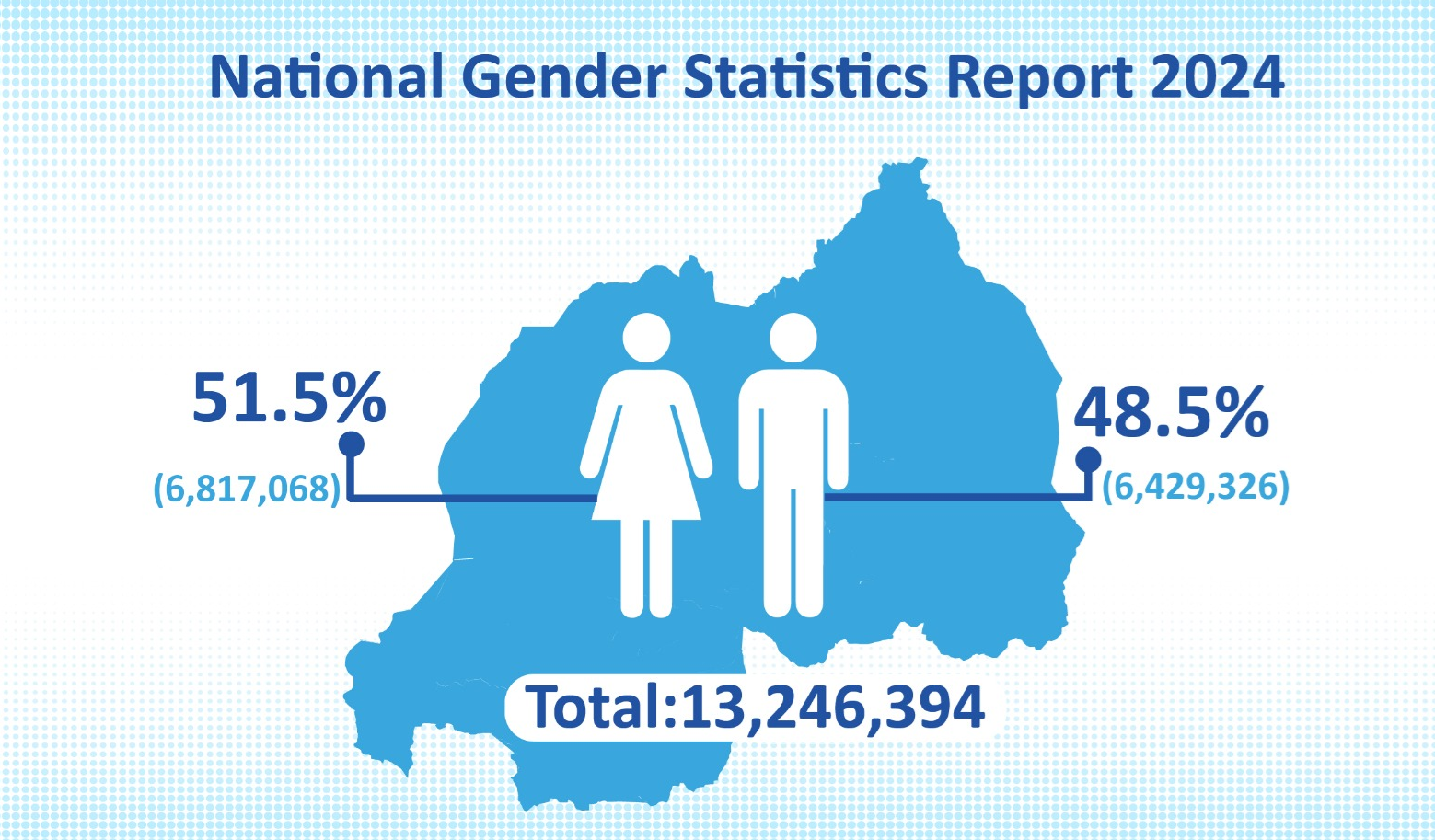
This is the sixth edition of the National Gender Statistics Report that provides updated sex-disaggregated data in the twelve areas adopted taking into consideration the Beijing declaration and platform for action. Specifically, the areas covered are: (1) population and youth, (2) agriculture, livestock and forestry, (3) income and access to finance, (4) infrastructure, ICTs and media, (5) trade and industry, (6) economic activity and time use, (7) environment and natural resources, (8) poverty and social protection, (9) health and nutrition, (10) education, (11) decision making and public life and, (12) justice and human rights.
According to the 5th RPHC, 68.9% of Rwandan households are engaged in agricultural activities and 94.8% of women farmers have access to land compared to 93.7% of men. With regard to access to finance, 85% of women saved money in 2020 while the same figure was 87% for men. By 2024, women’s formal non−bank savings grew from 44% to 53%, while men’s savings increased from 54% to 65%.
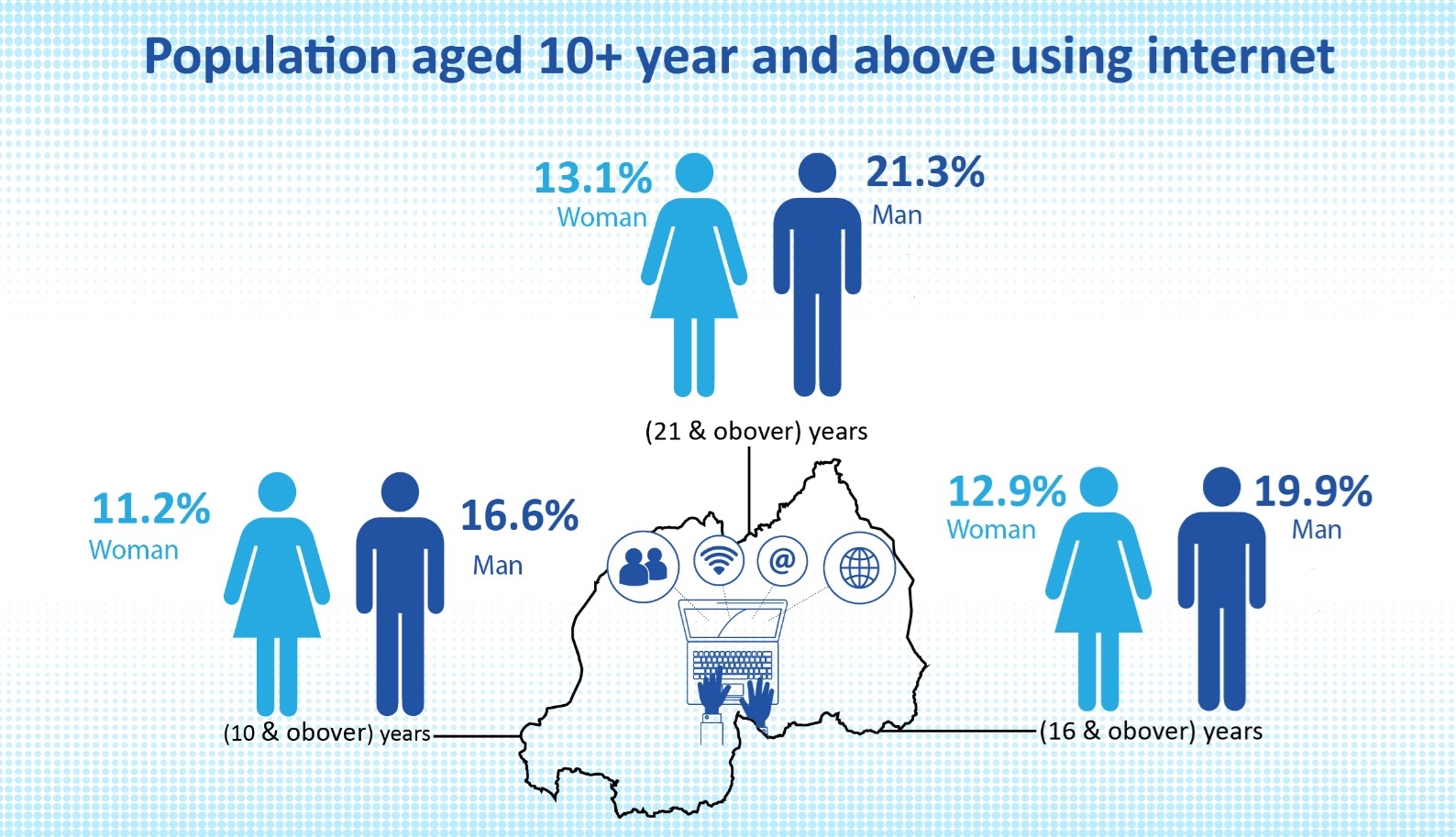
Bank loans for women increased from 7% to 8% in 2024 while for men, it rose from 10% to 13%. Ownership of dwellings among female−headed households was at 71.1% while access to improved drinking was at 81.4% by 2022. Among male headed households, these percentages were respectively 71.9% and 82.7%. The percentage of female− headed households using electricity for lighting rose from 11.9% in 2012 to 41.1% in 2022 while for male headed households, this percentage increased from 18.8% in 2012 to 49.6% in 2022 in the same period. Regarding computer literacy, 9.6% of women are computer literate compared to 14.7% of men.
The data show a downfall in women’s labor force participation, from 58.2% in 2020 to 52.2% in 2023, while men’s participation increased from 65.6% to 67.5%. Regarding time use, women spend more time on unpaid works, averaging 24 hours a week compared to 13.6 hours for men. In informal cross−border trade, women predominate with 69.2% involvement in 2022, while the rate was 30.8% for men.
In education, girls’ enrollment in lower secondary school increased from 54.1% in 2020/21 to 54.6% in 2022/23, while boys’ enrollment dropped from 45.9% to 45.4%. Girls’ enrollment rate in upper secondary was high with 59.3% while from boys the rate was 40.7%. However, in TVET enrollment for women fell from 46.7% in in 2020/21 to 43.4% in 2022/23 while for males, it increased from 53.3% to 56.6% in the same period. Female representation in higher education underwent a moderate decrease from 44.9% .2020/21 to 44.2% in 2022/23, while for males, it increased from 55.1% to 55.8%.
In governance, female representation in the cabinet decreased from 36.8% in 2014 to 31.25% in in 2024, while in the Chamber of deputies, women hold 63.3% of seats and 53.8% in the Senate by 2024. In the justice sector, 52% of primary court judges are women, while they occupy 48% of national prosecutors. The data show that media sector remains male−dominated, with 23.9% of accredited journalists being female.
