Kigali, April 2025 — The Rwanda Vital Statistics Report 2024 reveals important insights into the causes of death across the country, pointing to a growing burden of non-communicable diseases (NCDs), both in health facilities and in community settings.
Health Facility Deaths: Non-Communicable Diseases Lead
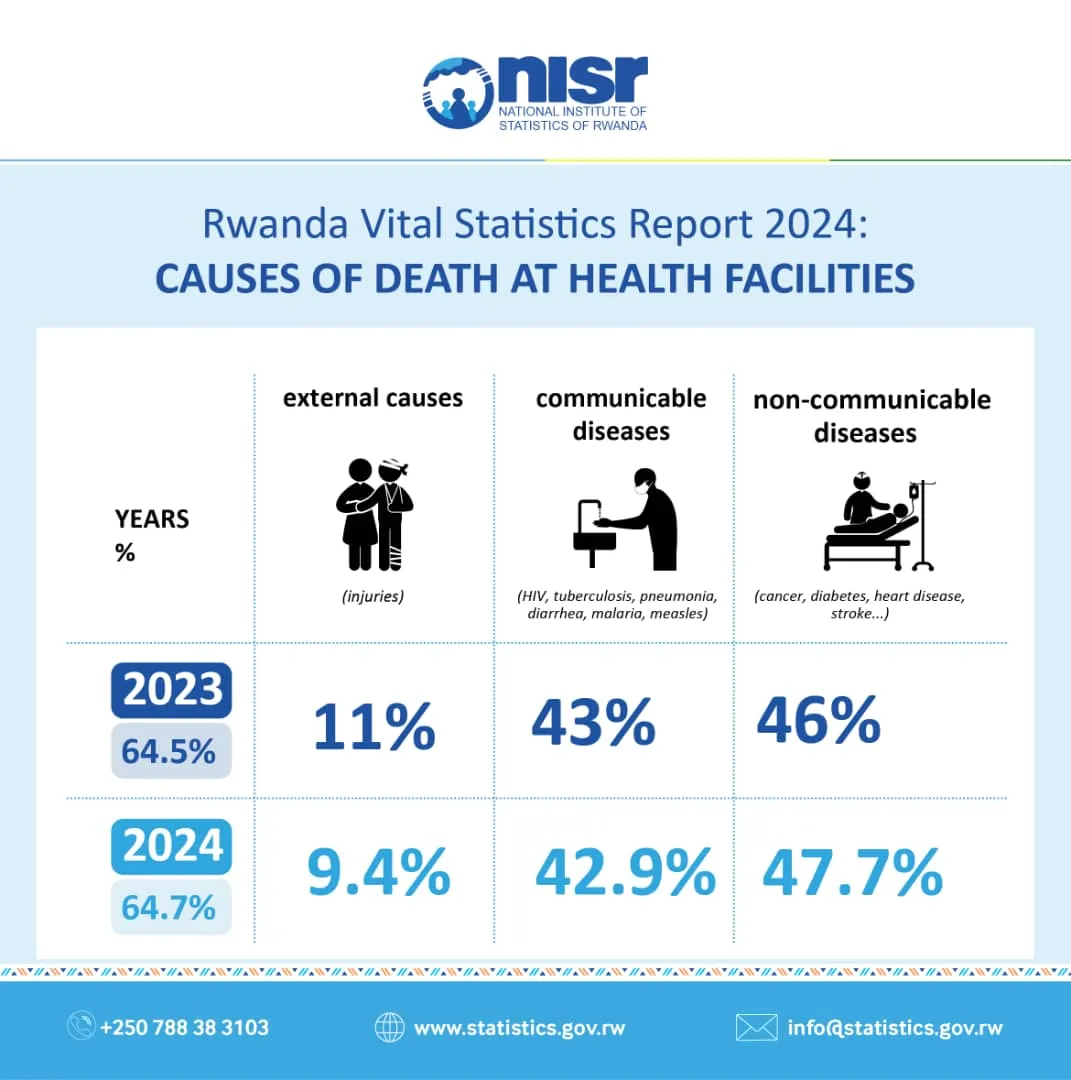
In 2024, 64.7% of all death records from health facilities contained usable information coded according to the international ICD-10 classification, a slight improvement from 64.5% in 2023. Among these, 47.7% were caused by non-communicable diseases such as diabetes, cardio-vascular disease, other metabolism diseases , cancer and mental health diseases, 42.9% were due to communicable diseases like HIV, Malaria, Hepatitis, Tuberculosis, pneumonia, etc. 9.4% resulted from external causes, including injuries and road traffic accidents.
These figures highlight a shifting trend in Rwanda’s disease burden, aligning with global patterns where non-communicable diseases increasingly lead to mortality. The data emphasize the need for sustained investment in preventive healthcare, early diagnosis, and lifestyle change related interventions.
Community Deaths: Drop in quality reported data, but Clear Trends
The proportion of usable cause-of-death data from community deaths decreased to 84.0% in 2024, down from 90.8% in 2023. Despite this decline, the breakdown of causes reveals significant trends: 59.3% were due to non-communicable diseases, 28.4% to communicable diseases and 12.3% to external causes such as injuries.
These findings point to the urgent need to improve health services at the community level. Strengthening access to care, raising awareness about chronic diseases, and investing in better reporting mechanisms are vital to capturing complete and accurate health data.
Why It Matters
This data plays a crucial role in shaping national health policies, resource allocation, and intervention strategies. It also reflects Rwanda’s progress in strengthening civil registration and vital statistics systems, which are key pillars of effective public health monitoring.
Accurate data on causes of death plays a crucial role in shaping national health policies in health sector, and key pillars of effective public health monitoring, and development partners to design effective health intervention strategies.
The 2024 report shows that while Rwanda continues to make progress in death registration and cause-of-death reporting, there is a need to increase both facilities and community death reporting into the CRVS system and addressing the growing challenge of non-communicable diseases.
As Rwanda continues its journey toward universal health coverage, the 2024 Rwanda Vital statistics report serves as a call to action for health professionals, policymakers, and citizens alike to prioritize health education, early detection, and improved healthcare access
We invite you to explore the detailed report through the link below https://statistics.gov.rw/publication/rwanda-vital-statistics-report-2024
Andre MATESO
Public Relation and Communication Officer
